A projectile is shot directly away from earth’s surface – A projectile shot directly away from Earth’s surface embarks on a captivating journey influenced by a myriad of factors. This article delves into the intricacies of initial velocity, trajectory, range, and time of flight, providing a comprehensive understanding of projectile motion.
Initial velocity, the speed and direction imparted to the projectile at launch, plays a crucial role in determining its trajectory. Gravity and air resistance, external forces acting on the projectile, shape its path as it ascends and descends.
Initial Velocity
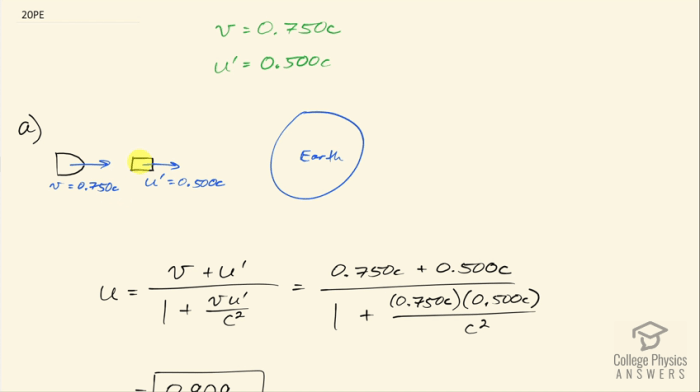
Initial velocity refers to the speed and direction of a projectile at the moment it is launched or released. It plays a crucial role in determining the trajectory, range, height, and time of flight of the projectile.
The initial velocity affects the projectile’s trajectory in several ways:
- Speed:A higher initial speed results in a longer range and higher maximum height.
- Direction:The angle of the initial velocity determines the angle of the projectile’s trajectory.
- Horizontal and Vertical Components:The initial velocity can be decomposed into horizontal and vertical components, which affect the horizontal range and vertical height, respectively.
Factors influencing initial velocity include:
- Force applied:The greater the force applied to the projectile, the higher the initial velocity.
- Mass of the projectile:A heavier projectile will have a lower initial velocity for the same force applied.
- Launch angle:The launch angle can affect the initial velocity’s horizontal and vertical components.
Trajectory
The trajectory of a projectile shot directly away from Earth’s surface is a parabolic path. It is determined by the initial velocity and the gravitational force acting on the projectile.
Factors affecting the trajectory include:
- Initial velocity:A higher initial velocity results in a longer and flatter trajectory.
- Gravity:The gravitational force pulls the projectile downward, causing it to follow a parabolic path.
- Air resistance:Air resistance can cause the projectile to deviate from its parabolic path, especially for low-velocity projectiles.
| Initial Velocity | Trajectory |
|---|---|
| High | Long, flat trajectory |
| Medium | Moderately curved trajectory |
| Low | Steeply curved trajectory |
Range
The range of a projectile is the horizontal distance it travels before hitting the ground. It is affected by the initial velocity and the trajectory.
The formula to calculate the range (R) of a projectile is:
R = (v2
sin(2θ)) / g
- v is the initial velocity
- θ is the launch angle
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s 2)
Height
The maximum height reached by a projectile is determined by its initial velocity and the gravitational force. A higher initial velocity results in a higher maximum height.
Factors influencing the maximum height include:
- Initial velocity:A higher initial velocity leads to a higher maximum height.
- Launch angle:The launch angle affects the vertical component of the initial velocity, which influences the maximum height.
- Gravity:Gravity pulls the projectile downward, limiting its maximum height.
| Initial Velocity | Maximum Height |
|---|---|
| High | High maximum height |
| Medium | Moderate maximum height |
| Low | Low maximum height |
Time of Flight
The time of flight is the total time a projectile spends in the air, from launch to landing. It is affected by the initial velocity and the trajectory.
The formula to calculate the time of flight (t) of a projectile is:
t = (2
- v
- sin(θ)) / g
- v is the initial velocity
- θ is the launch angle
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s 2)
FAQ Corner: A Projectile Is Shot Directly Away From Earth’s Surface
What is the effect of initial velocity on the trajectory of a projectile?
Initial velocity significantly impacts the trajectory of a projectile. Higher initial velocities result in higher maximum heights and longer ranges, while lower initial velocities lead to shorter trajectories.
How does gravity affect the motion of a projectile?
Gravity is the primary force acting on a projectile, causing it to accelerate downward. This downward acceleration affects the projectile’s trajectory, causing it to follow a parabolic path.
What is the formula for calculating the range of a projectile?
The range of a projectile can be calculated using the formula: Range = (Initial Velocity)^2 – sin(2 – Launch Angle) / Gravity.