Adding subtracting and multiplying polynomials worksheet – The Adding, Subtracting, and Multiplying Polynomials Worksheet serves as an invaluable resource for students seeking to master the fundamental operations of polynomial algebra. This meticulously crafted worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of polynomial basics, addition, subtraction, and multiplication, empowering learners with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate polynomial expressions with confidence.
Delving into the intricacies of polynomials, the worksheet unravels the concepts of terms, coefficients, and degrees, laying the foundation for understanding polynomial operations. Through illustrative examples, learners grasp the properties of polynomials, including their leading coefficients and constant terms. Equipped with this foundational knowledge, the worksheet guides students through the processes of adding, subtracting, and multiplying polynomials, employing clear and concise explanations coupled with ample practice problems.
Polynomial Basics: Adding Subtracting And Multiplying Polynomials Worksheet
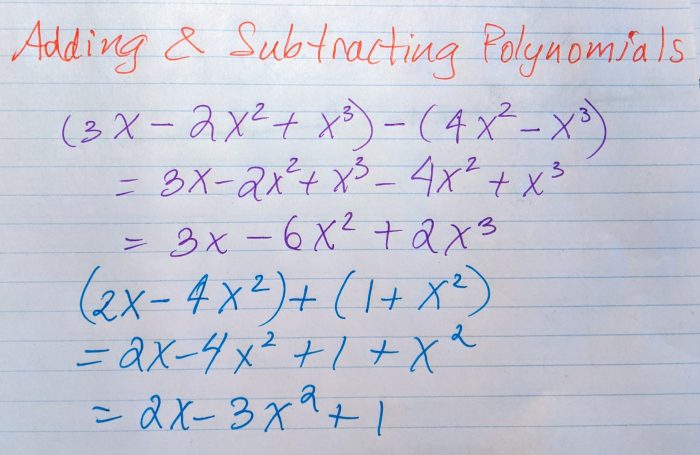
Polynomials are algebraic expressions that consist of terms, each containing a variable raised to a non-negative integer power and multiplied by a coefficient. The terms are added or subtracted to form the polynomial.
The degree of a polynomial is the highest exponent of the variable in the polynomial. The leading coefficient is the coefficient of the term with the highest degree. The constant term is the term that does not contain any variable.
Adding Polynomials
To add polynomials, align the like terms vertically and add their coefficients. The like terms are terms that have the same variable and exponent.
For example:
- (x 2+ 2x + 3) + (x 2– x + 5) = 2x 2+ x + 8
- (3x 3– 2x 2+ 5x) + (x 3+ x 2– 3x) = 4x 3– x 2+ 2x
Subtracting Polynomials
To subtract polynomials, change the subtraction to addition and change the signs of the terms being subtracted.
For example:
- (x 2+ 2x + 3) – (x 2– x + 5) = (x 2+ 2x + 3) + (-x 2+ x – 5) = 2x + 8
- (3x 3– 2x 2+ 5x) – (x 3+ x 2– 3x) = (3x 3– 2x 2+ 5x) + (-x 3– x 2+ 3x) = 2x 3– 3x 2+ 8x
Multiplying Polynomials
There are two common methods for multiplying polynomials: the distributive property and the FOIL method.
Distributive Property:Multiply each term in the first polynomial by each term in the second polynomial and add the products.
FOIL Method:Multiply the first terms, the outer terms, the inner terms, and the last terms of the two polynomials and add the products.
For example:
- (x + 2)(x – 3) = x 2– 3x + 2x – 6 = x 2– x – 6
- (2x 2– 3x + 5)(x – 1) = 2x 3– 2x 2– 3x 2+ 3x + 5x – 5 = 2x 3– 5x 2+ 8x – 5
Worksheet Design, Adding subtracting and multiplying polynomials worksheet
Create a table with columns for polynomials, operations, and solutions. Include clear instructions and examples for students to follow.
Answer Key
Provide a detailed answer key for the worksheet, explaining each step of the operations. Include explanations for any special cases or exceptions encountered in the problems.
General Inquiries
What is a polynomial?
A polynomial is an algebraic expression consisting of variables and coefficients, combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication operations.
How do you add polynomials?
To add polynomials, align them vertically and combine like terms by adding their coefficients.
How do you subtract polynomials?
To subtract polynomials, change the subtraction operation to addition and change the sign of the polynomial being subtracted.
How do you multiply polynomials?
Polynomials can be multiplied using the distributive property or the FOIL method.