Navigating the body planes directions positions and movements is a fundamental aspect of understanding human anatomy and physiology. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the three primary body planes, six cardinal directions, and anatomical position, providing a solid foundation for exploring body movements, their axes, and the role of joints and muscles in facilitating these movements.
Understanding body planes and directions is not only crucial for healthcare professionals but also for fitness instructors, yoga practitioners, dancers, and athletes. This guide explores practical applications of these concepts in medical imaging, everyday activities, and various fields of study.
Navigating the Body Planes, Directions, Positions, and Movements: Navigating The Body Planes Directions Positions And Movements
Understanding the human body’s planes, directions, positions, and movements is essential for healthcare professionals, fitness trainers, and individuals involved in physical activities. This knowledge provides a standardized framework for describing and analyzing body structures and functions.
Understanding Body Planes, Directions, and Positions, Navigating the body planes directions positions and movements
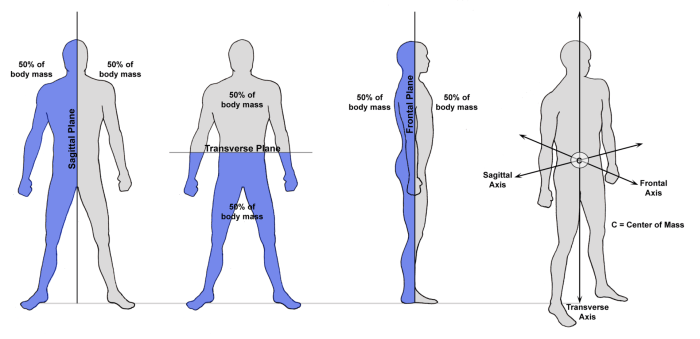
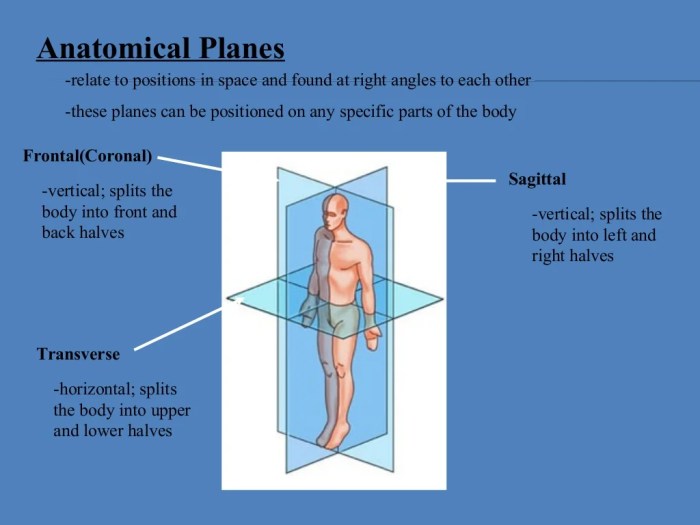
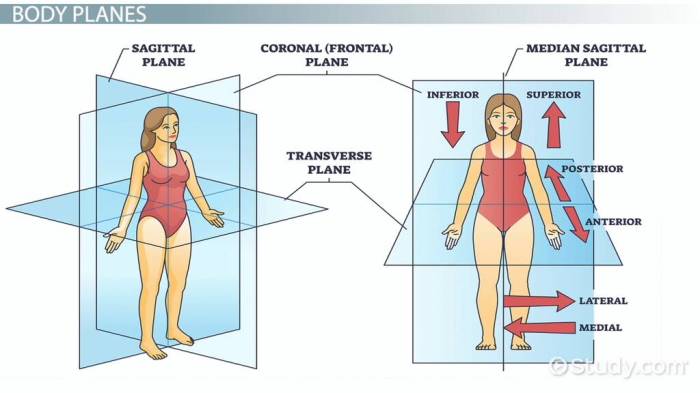
The body has three primary planes that divide it into sections: the sagittal plane, frontal plane, and transverse plane. The sagittal plane runs vertically, dividing the body into left and right halves. The frontal plane runs vertically, dividing the body into front and back halves.
The transverse plane runs horizontally, dividing the body into upper and lower halves.
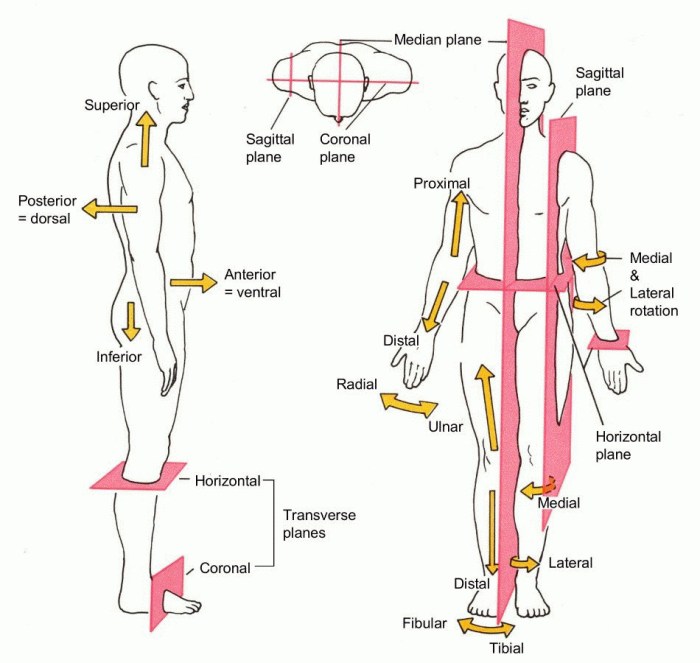
Six cardinal directions are used to describe body locations: anterior (front), posterior (back), superior (above), inferior (below), medial (towards the midline), and lateral (away from the midline). The anatomical position is a standardized posture used to describe body parts and movements.
It involves standing upright with the arms at the sides and palms facing forward.
Navigating Body Movements
Body movements occur around axes that are perpendicular to the body planes. The sagittal axis runs vertically through the center of the body. The frontal axis runs horizontally from side to side. The transverse axis runs horizontally from front to back.
Body movements are classified into several types, including flexion (bending forward), extension (bending backward), abduction (moving away from the midline), and adduction (moving towards the midline). Joints and muscles work together to facilitate body movements.
Applying Body Planes and Directions in Practice
Body planes and directions are used extensively in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays and MRIs to visualize and diagnose anatomical structures. Understanding body planes and directions is also crucial for healthcare professionals to accurately describe patient conditions and treatment plans.
In fitness and exercise, knowledge of body planes and directions is essential for designing effective exercise programs and ensuring proper form. It helps individuals target specific muscle groups and improve movement efficiency.
Creating Illustrations and Visual Aids
Tables, illustrations, and diagrams can enhance understanding of body planes, directions, and movements. Tables can summarize the planes, directions, and movements discussed. Illustrations and diagrams can depict anatomical landmarks and demonstrate body movements from different perspectives.
Questions and Answers
What are the three primary body planes?
The three primary body planes are the sagittal plane, frontal plane, and transverse plane.
What is the anatomical position?
The anatomical position is a standardized reference position used to describe body structures and movements. It involves standing upright with the arms at the sides and the palms facing forward.
What is the difference between flexion and extension?
Flexion is the bending of a joint, while extension is the straightening of a joint.